Saturday, 11 August 2012
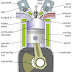
Piston
Do you like this story?
 |
| Piston (Image credit: btechgurus.blogspot.com) |
Material for Piston:
The material used for piston is mainly aluminium alloy. Aluminium pistons can be either cast or forged. Cast iron is also used for piston.
Piston Clearance:
Pistons are usually small in diameter than the bore of the cylinder. The space between the piston and the cylinder wall is called the piston clearance. This clearance is essentially for the following reasons:
- It provides a space for a film of lubricant between the piston and cylinder wall to reduce friction.
- It prevents piston seizure due to very high operating temperature, piston and cylinder block expand the cylinder is cooled better than the piston, hence sufficient clearance should be provided for the piston to expand, fail in which the piston seizure will result.
- If there is no clearance between the piston and cylinder, it will be impossible for the piston to reciprocate in the cylinder.
The amount of piston clearance depends upon the size of the cylinder bore and the metal used in the piston. It is generally 0.025 mm to 0.100 mm
Piston head shape or piston crown:
 |
| Piston heads (Image credit: miata.net) |
The piston head is often flat but may be shaped to suit the combustion chamber. The combustion space can be controlled by dishing or doming the piston crown and recess for the valve heads can also be machined into the crown. The compression ratio can be more accurately controlled by machining the combustion chamber in the piston, but it means that most of the heat of combustion has to be dissipated through the piston in stead of the cylinder head.

This post was written by: Sanjay Verma
Sanjay Verma is an experienced mechanical engineer and a lecturer. In this blog he shares his knowledge about various subjects of mechanical engineering. Follow him on Google+